State of Preschool
Washington
Access Rankings
Resource Rankings
Total Benchmarks Met
Overview

During the 2022-2023 school year Washington’s Department of Children, Youth, and Families (DCYF) enrolled 15,808 children in the Early Childhood Education and Assistance Program (ECEAP), an increase of 801 children from the prior year. State spending for ECEAP totaled $177,228,389 with an additional $4,605,000 in federal recovery funding to support the program, up $8,614,391 (5%), adjusted for inflation, since last year. State spending per child on ECEAP equaled $11,503 (including recovery dollars) in 2022-2023, down $40 from 2021-2022, adjusted for inflation. Washington ECEAP met 9 of 10 quality standards benchmarks.
Washington’s Office of Superintendent of Public Instruction (OSPI) also served 5,244 children in a Transitional Kindergarten (TK) program during the 2022-2023 school year, up 2,117 children from the prior year. State spending for TK was $69,532,084, an increase of $28,345,101 (69%), adjusted for inflation, since last year. State spending per child on TK was $13,259, up $88 from 2021-2022, adjusted for inflation. TK met 6 out of 10 quality standards benchmarks.
What's New
ECEAP added 800 more slots during the 2022-2023 school year and another 500 in 2023-2024 as well as 1,000 part- to full-day conversions. In 2022-2023, a 1.6% slot rate increase also took effect. In 2023-2024 contractors received additional increases: 18% for school-day slots, 9% for working-day slots, and 7% for part-day slots. Summer ECEAP was funded by the state legislature for the first time and was provided by 21 ECEAP contractors to 1,948 students in the summer of 2022. The state also helped to fund 178 Early ECEAP slots for children birth to age three after the PDG B-5 grant ended in December 2022. The legislature also funded $7 million for the Tribal Early Learning Fund to provide critical, culturally sensitive services.
Income eligibility was expanded and moved to State Median Income (SMI) instead of Federal Poverty Level (FPL) in 2021-2022. Income eligibility categories will increase again in 2030-2031. The state QRIS implemented a revised quality recognition and improvement system based on provider feedback that moves to a virtual data collection model that allows reviewers the opportunity to see every teaching environment and engage in coaching with teachers.
The Department of Children, Youth, and Families (DCYF) and the Office of the Superintendent of Public Instruction (OSPI) are supporting TK programs with TA on collaborating with community-based partners (including ECEAP), Head Start, child care, family child care, and licensed tribally-led early learning programs. DCYF and OSPI jointly identified strategies to improve alignment of high quality preschool across the two agencies and increase equitable access to preschool.
Background
In 2018, the Washington Department of Early Learning merged into the new Department of Children, Youth, and Families (DCYF), which oversees early learning programs along with child welfare and juvenile rehabilitation. One of the five strategic priorities for DCYF is to create a high-quality integrated birth to eight system. This includes expanding access to infant/toddler supports, expanding access to affordable, high-quality care, creating a responsive and inclusive integrated pre-k system, and expanding supports to the early learning workforce. The state ECEAP, created in 1985, is a large part of the state’s strategy to accomplish this goal. In recent years, both funding and enrollment for ECEAP have been growing. ECEAP funding comes from the state general fund, the Education Legacy Trust Account funded by estate taxes, and the “opportunity pathways account” financed by lottery proceeds. In 2010, the state Legislature established the ECEAP as a statutory entitlement for all eligible children, not funded by Head Start, by the 2018-2019 school year — a deadline extended to 2026-2027. ECEAP focuses on the whole child and provides comprehensive nutrition, health, education and family support services to Washington’s most at-risk young children. To be eligible for ECEAP currently, children must be 3- or 4-years-old and live in households with an income at or below 36% of the SMI for non-tribal children or 100% SMI for tribal children, eligible for special education services, experiencing homelessness, or previously participated in an approved birth to three early learning programs. Up to 10% of ECEAP enrollment may include children whose families do not meet the poverty requirement but experience other risk factors that could jeopardize learning, development, or school success.
The Office of Superintendent of Public Instruction (OSPI) is the primary agency charged with overseeing public K–12 education in Washington state. Working with the state’s 295 public school districts and six state-tribal education compact schools, OSPI allocates funding and provides tools, resources, and technical assistance so every student in Washington is provided a high-quality public education. The goal of Washington’s K–12 education system is to prepare every student for postsecondary pathways, careers, and civic engagement.
OSPI’s Transitional Kindergarten (TK) is a kindergarten program for children aged 5 who have missed the cutoff for kindergarten or are turning 5 before the following school year and do not have access to high-quality early learning experiences prior to kindergarten. Districts may offer TK programs, but they are not required to do so. The requirements for TK are the same as those for regular kindergarten established by RCW 28A.150.315. While school districts in Washington have always had the ability to enroll children into kindergarten early, TK has gained momentum in recent years, as a strategy for closing opportunity gaps.
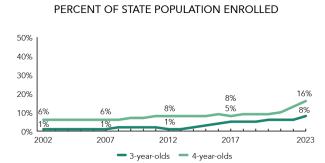
Washington’s overall support for state-funded preschool is depicted in the first two sections of this state profile. The third section focuses on ECEAP and the fourth section on TK.
-
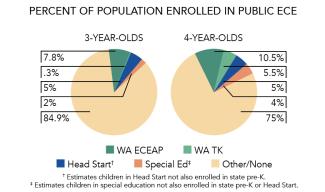
Access
Total state pre-K enrollment 21,052 Special education enrollment, ages 3 and 4 9,665 Federally funded Head Start enrollment, ages 3 and 4 9,361 State-funded Head Start enrollment, ages 3 and 4 0 Resources
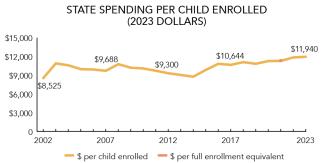
Total state pre-K spending $251,365,473 State Head Start spending $0 State spending per child enrolled $11,940 All reported spending per child enrolled* $13,096 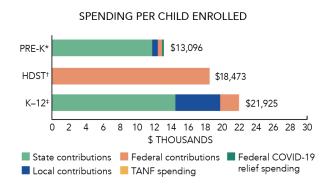
*Pre-K programs may receive additional funds from federal or local sources that are not included in this figure. †Head Start per-child spending includes funding only for 3- and 4-year-olds. ‡K–12 expenditures include capital spending as well as current operating expenditures.
-
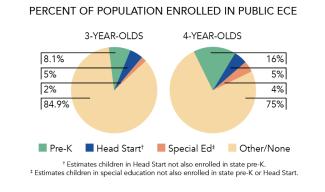
Access
Resources
Total state pre-K spending $181,833,389 Local match required? No State spending per child enrolled $11,503 All reported spending per child enrolled* $11,503 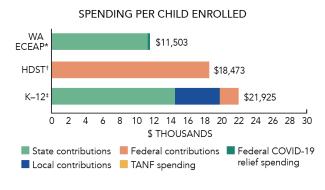
*Pre-K programs may receive additional funds from federal or local sources that are not included in this figure. †Head Start per-child spending includes funding only for 3- and 4-year-olds. ‡K–12 expenditures include capital spending as well as current operating expenditures.
Washington Early Childhood Education and Assistance Program (ECEAP) Quality Standards Checklist
| Policy | WA ECEAP Requirement | Benchmark | Meets Benchmark? |
|---|---|---|---|
For more information about the benchmarks, see the Executive Summary and the Roadmap to State pages. | 9benchmarks met | ||
| Early Learning & Development Standards Benchmark | Comprehensive, aligned, supported, culturally sensitive | Comprehensive, aligned, supported, culturally sensitive | |
| Curriculum Supports Benchmark | Approval process & supports | Approval process & supports | |
| Teacher Degree Benchmark | AA | BA | |
| Teacher Specialized Training Benchmark | ECE, CD, ECE SpEd | Specializing in pre-K | |
| Assistant Teacher Degree Benchmark | CDA | CDA or equivalent | |
| Staff Professional Development Benchmark | 20 hours/year (teachers), 15 hours/year (assistants); PD plans; Coaching | For teachers & assistants: At least 15 hours/year; individual PD plans; coaching | |
| Maximum Class Size Benchmark | 20 (3- & 4-year-olds) | 20 or lower | |
| Staff to Child Ratio Benchmark | 1:10 (3- & 4-year-olds) | 1:10 or better | |
| Screening & Referral Benchmark | Vision, hearing, health & more | Vision, hearing & health screenings; & referral | |
| Continuous Quality Improvement System Benchmark | Structured classroom observations; Data used for program improvement | Structured classroom observations; data used for program improvement | |
-
Access
Resources
Total state pre-K spending $69,532,084 Local match required? No State spending per child enrolled $13,259 All reported spending per child enrolled* $17,900 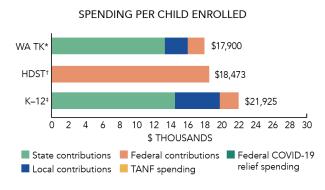
*Pre-K programs may receive additional funds from federal or local sources that are not included in this figure. †Head Start per-child spending includes funding only for 3- and 4-year-olds. ‡K–12 expenditures include capital spending as well as current operating expenditures.
Washington Transitional Kindergarten (TK) Quality Standards Checklist
| Policy | WA TK Requirement | Benchmark | Meets Benchmark? |
|---|---|---|---|
For more information about the benchmarks, see the Executive Summary and the Roadmap to State pages. | 6benchmarks met | ||
| Early Learning & Development Standards Benchmark | Comprehensive, aligned, supported, culturally sensitive | Comprehensive, aligned, supported, culturally sensitive | |
| Curriculum Supports Benchmark | Approval process & supports | Approval process & supports | |
| Teacher Degree Benchmark | BA | BA | |
| Teacher Specialized Training Benchmark | ECE, Elem. Ed., ECE SpEd, SpEd | Specializing in pre-K | |
| Assistant Teacher Degree Benchmark | HSD | CDA or equivalent | |
| Staff Professional Development Benchmark | 100 hours/5 years (teachers), 3 days/year (assistants); PD plans; Coaching | For teachers & assistants: At least 15 hours/year; individual PD plans; coaching | |
| Maximum Class Size Benchmark | No limit (3- & 4-year-olds) | 20 or lower | |
| Staff to Child Ratio Benchmark | No limit (3- & 4-year-olds) | 1:10 or better | |
| Screening & Referral Benchmark | Vision, hearing, health & more | Vision, hearing & health screenings; & referral | |
| Continuous Quality Improvement System Benchmark | Structured classroom observations; Data used for program improvement | Structured classroom observations; data used for program improvement | |