State of Preschool
Kentucky
Access Rankings
Resource Rankings
Total Benchmarks Met

Overview
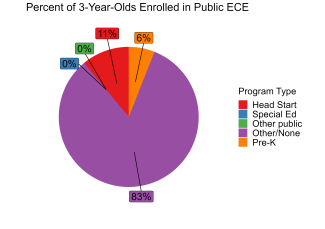
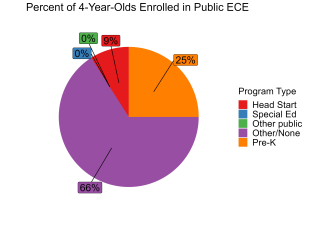
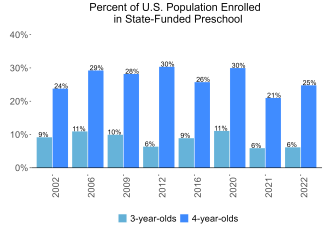
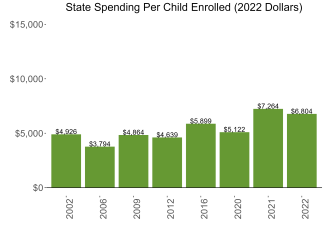
During the 2021-2022 school year. Kentucky preschool enrolled 17,611 children, an increase of 2,187 from the prior year, as the program began to recover from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. State spending totaled $100,739,010 with an additional $19,081,493 in federal recovery funds to support the program, up $7,785,654 (7%), adjusted for inflation since last year. State spending per child (including federal recovery funds) equaled $6,804 in 2021-2022, down $460 from 2020-2021, adjusted for inflation. Kentucky met 8 of 10 quality standards benchmarks.
What's New
In December 2022, Kentucky was awarded a federal Preschool Development Grant Birth through Five (PDG B–5) renewal grant for $11,990,400. Funds will be used to refresh Kentucky’s needs assessment and strategic plan; support family engagement; document exemplar practices, opportunities, and gaps; and effectively transition children across the continuum of educational milestones, prioritizing highly vulnerable and un- or under-served children. With this grant, Kentucky will support working families to ensure children have a strong start in school and life and grow Kentucky’s economy in the process.
Enrollment in the Kentucky Preschool Program (KPP) increased for the first time since the pandemic, which may be a result of recruitment and retention activities discussed by the Commissioner’s Preschool Coordinator Advisory Group. In June 2022, the state’s revised Early Childhood Standards and Family Guides were officially launched and are aligned with the Kentucky Academic Standards and include supports for dual language learners and additional resources.
During the pandemic, including the 2021-2022 school year, participation in All STARS (QRIS) was not monitored and ECERS data were not collected. In 2022-2023, program quality data were collected again for planning purposes. In September 2021, the Kentucky General Assembly passed Senate Bill 1 (SB1), an act relating to the delivery of education and care for children and declaring an emergency. SB1 provides supports and flexibilities for schools during the pandemic. The state developed guidance to support school districts with implementation of SB1, which includes support for preschool students.
Using federal recovery funds, the Office of Special Education and Early Learning (OSEEL) is implementing a project for delivering high-quality training and coaching to preschool through third grade (P–3) staff and administrators designed to improve learning outcomes of young children that were disproportionately impacted by the ongoing pandemic. The project includes hiring statewide trainers and coaches with backgrounds in early literacy, early mathematics, positive approaches to behavior and discipline, and/or high-quality preschool.
Background
The Kentucky Preschool Program (KPP), launched in 1990, is available to 4-year-olds from low-income families, and 3- and 4-year-olds with disabilities. KPP programs operate half- or full-day, for at least 2.5 hours per day, four or five days per week. Income eligibility increased from 150% to 160% of FPL beginning with the 2015-2016 school year. Children who do not meet state eligibility requirements may still participate if there is space, but they are funded either by the school district or tuition rather than state dollars.
KPP is administered by the Kentucky Department of Education (KDE), Office of Special Education and Early Learning, School Readiness Branch. Funds are distributed to school districts through a funding formula. School districts may subcontract with private child care centers, Head Start programs, and special education providers to offer preschool services.
Kentucky Preschool Program
Access
Resources
| Total state pre-K spending | $119,820,503 |
| Local match required? | No |
| State Head Start spending | $0 |
| State spending per child enrolled | $6,804 |
| All reported spending per child enrolled* | $11,505 |
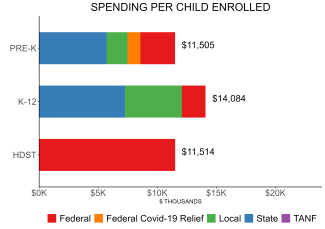
Pre-K programs may receive additional funds from federal or local sources that are not included in this figure. K–12 expenditures include capital spending as well as current operating expenditures. Head Start per-child spending includes funding only for 3- and 4-year-olds.
Kentucky Quality Standards Checklist
| Policy | Requirement | Benchmark | Meets Benchmark? |
|---|---|---|---|
For more information about the benchmarks, see the Executive Summary and the Roadmap to State pages. | 8benchmarks met | ||
| Early Learning & Development Standards Benchmark | Comprehensive, aligned, supported, culturally sensitive | Comprehensive, aligned, supported, culturally sensitive | |
| Curriculum Supports Benchmark | Approval process & supports | Approval process & supports | |
| Teacher Degree Benchmark | BA | BA | |
| Teacher Specialized Training Benchmark | ECE, CD, ECE SpEd | Specializing in pre-K | |
| Assistant Teacher Degree Benchmark | HSD | CDA or equivalent | |
| Staff Professional Development Benchmark | 24 hours/year (teachers); 18 hours/year (assistants); PD plans (public teachers only); Coaching (certified teachers) | For teachers & assistants: At least 15 hours/year; individual PD plans; coaching | |
| Maximum Class Size Benchmark | 20 (3- & 4-year-olds) | 20 or lower | |
| Staff to Child Ratio Benchmark | 1:10 (3- & 4-year-olds) | 1:10 or better | |
| Screening & Referral Benchmark | Vision, hearing, health & more | Vision, hearing & health screenings; & referral | |
| Continuous Quality Improvement System Benchmark | Structured classroom observations; Data used for program improvement | Structured classroom observations; data used for program improvement | |