State Support for Head Start Over the Years
March 27, 2012
In addition to offering state pre-K and child care subsidies some states support pre-K by adding on to the federal Head Start program. Supplementing Head Start programs with state funding allows states to build upon the federal Head Start program–funding more children, providing extended-day and/or extended-year services, or making quality improvements. This is especially important for several states that don’t otherwise fund pre-K at the state level. In 2009-2010 this included Idaho and New Hampshire. Delaware, Minnesota, and Oregonserved enough additional children through their Head Start state supplements for these to qualify as de facto state pre-K programs by NIEER’s definition.
It’s been a long time since we’ve looked longitudinally at states’ supplements to the federal Head Start program. Unfortunately, we haven’t had good news to report. Data from The State of Preschool 2010 indicate that states have cut funding and serve fewer children since we started tracking these numbers in The State of Preschool: 2003 State Preschool Yearbook.
Between fiscal years 2002 and 2010, the total number of states supplementing Head Start dipped only from 17 to 16, with Indiana and Ohio halting state funding of Head Start programs while Idaho began providing a state supplement. In addition, Hawaii began funding a state supplement to Head Start in the 2003-2004 school year, but then stopped this funding in the 2007-2008 school year. Overall, as indicated in Table 1, adjusted and nominal spending, as well as enrollment, have all declined in this time period; adjusted spending was nearly cut in half.
Table 1: Changes in Head Start Supplements, 2001-2002 to 2009-2010
Changes, 2001-2002 to 2009-2010 | ||
| Spending (2010 $) | -$122,028,988 | -45% |
| Nominal Spending | -$48,221,791 | -25% |
| Enrollment, 3s and 4s | -10,968 | -39% |
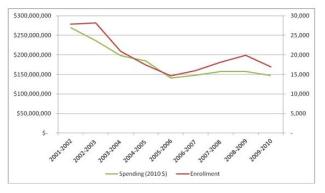
As shown in Table 2, the decreases took place at the beginning of the last decade, followed by an uptick until the 2009-2010 school year when it is likely that the recession started taking its toll.
Table 2: Longitudinal Changes in Head Start State Supplements

As we prepare for the release of the 2011 edition of the State Preschool Yearbook, we are seeing more of this downward trend. States are reporting less support for the 2010-2011 school year and are indicating that the 2011-2012 school year will fare even worse. Some states are completely eliminating their supplement to the federal program as a budget closing measure. This could present a double-whammy as stimulus money that benefitted federal Head Start is simultaneously disappearing at a time when the high child poverty rate makes clear how much young learners need these services. Stay tuned for when The State of Preschool 2011 is released on April 10th.
– Jen Fitzgerald, Public Information Officer, NIEER
– Megan Carolan, Policy Research Coordinator, NIEER
About NIEER
The National Institute for Early Education Research (NIEER) at the Graduate School of Education, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, NJ, conducts and disseminates independent research and analysis to inform early childhood education policy.
