State of Preschool
West Virginia
Access Rankings
Resource Rankings
Total Benchmarks Met

Overview
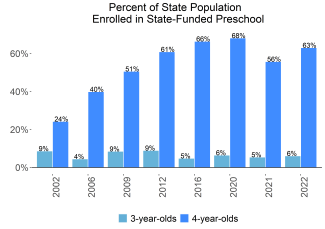
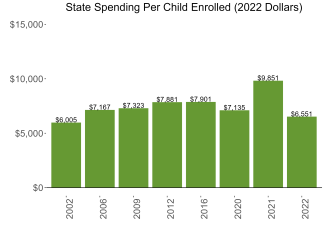
During the 2021-2022 school year, West Virginia preschool enrolled 13,268 children, an increase of 1,287 from the prior year, as the program began to recover from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. State spending totaled $80,436,415 and an additional $6,181,701 in TANF funds and $304,069 in federal recovery funds supported the program, down $31,103,846 (26%), adjusted for inflation since last year. State spending per child equaled $6,551 in 2021-2022, down $3,300 from 2020-2021, adjusted for inflation. Pre-k spending is calculated based on the previous year’s (2020-2021) enrollment which was lower due to the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in lower spending in 2021-2022. West Virginia met 9 of 10 quality standards benchmarks.
What's New
With decreased enrollment due to the COVID-19 pandemic, West Virginia continues to focus on increasing participation in the universal pre-K program and collaboration among the early childhood community to support families of young children even before entering pre-K.
In December 2022, West Virginia was awarded a federal Preschool Development Grant Birth through Five (PDG B–5) one-year planning grant for $2 million. The state plans to use this opportunity to enhance a coordinated system of early care and education by further strengthening connections of the collaborative pre-K program and programs serving children and families birth to pre-K, including enhanced transitions services.
Background
West Virginia introduced public preschool in 1983 for 3- and 4-year-olds through the Public School Early Childhood Education program. In 2002, legislation passed that required pre-K to be available to all 4-year-olds by 2012. Today, West Virginia’s Universal Pre-K System provides pre-K programs in all 55 counties in the state, serving 4-year-olds, as well as some 3-year-olds with special needs, and some kindergarten-eligible children if it is determined that kindergarten placement is not in the child’s best interest.
Public schools receive West Virginia Universal Pre-K funding directly, with half of all programs required to partner with child care centers, private pre-K, or Head Start agencies to meet demand. During the 2021-2022 school year, the collaboration rate was 83%. Programs are permitted to use additional funding from IDEA and federal Head Start.
As of July 2013, all new lead teachers in nonpublic settings are required to have at least a BA in ECE or a related field and, as of July 2014, all assistant teachers are required to apply for the Early Childhood Classroom Assistant Teacher Authorization, which requires a CDA or equivalent, as determined by the West Virginia Board of Education. West Virginia also increased instructional days per year and hours per week to at least 1,500 minutes (25 hours) of instruction per week and 48,000 minutes (800 hours) of instruction per year. Programs must operate no fewer than four days per week.
The West Virginia Universal Pre-K program had undergone a multi-year study to assess the effects of program participation. Programs develop monitoring systems to offer ongoing continuous quality improvement, using reliable monitoring tools selected by a local collaborative team. Children are assessed three times per year using the Early Learning Scale, and this information is used to track child and program outcomes over time, guide teacher professional development and coaching, adjust instructional practices, and support school readiness.
West Virginia Universal Pre-K
Access
Resources
| Total state pre-K spending | $86,922,185 |
| Local match required? | No |
| State Head Start spending | $0 |
| State spending per child enrolled | $6,551 |
| All reported spending per child enrolled* | $10,189 |
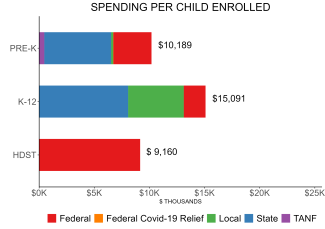
Pre-K programs may receive additional funds from federal or local sources that are not included in this figure. K–12 expenditures include capital spending as well as current operating expenditures. Head Start per-child spending includes funding only for 3- and 4-year-olds.
WV Quality Standards Checklist
| Policy | Requirement | Benchmark | Meets Benchmark? |
|---|---|---|---|
For more information about the benchmarks, see the Executive Summary and the Roadmap to State pages. | 9benchmarks met | ||
| Early Learning & Development Standards Benchmark | Comprehensive, aligned, supported, culturally sensitive | Comprehensive, aligned, supported, culturally sensitive | |
| Curriculum Supports Benchmark | Approval process & supports | Approval process & supports | |
| Teacher Degree Benchmark | BA | BA | |
| Teacher Specialized Training Benchmark | ECE, CD, ECE SpEd | Specializing in pre-K | |
| Assistant Teacher Degree Benchmark | CDA | CDA or equivalent | |
| Staff Professional Development Benchmark | 15 hours/year; PD plans; Coaching (classrooms collaborating with Head Start) | For teachers & assistants: At least 15 hours/year; individual PD plans; coaching | |
| Maximum Class Size Benchmark | 20 (3- & 4-year-olds) | 20 or lower | |
| Staff to Child Ratio Benchmark | 1:10 (3- & 4-year-olds) | 1:10 or better | |
| Screening & Referral Benchmark | Vision, hearing, health & more | Vision, hearing & health screenings; & referral | |
| Continuous Quality Improvement System Benchmark | Structured classroom observations; Data used for program improvement | Structured classroom observations; data used for program improvement | |

