State of Preschool
Vermont
Access Rankings
Resource Rankings
Total Benchmarks Met

Overview
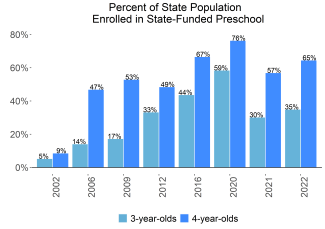
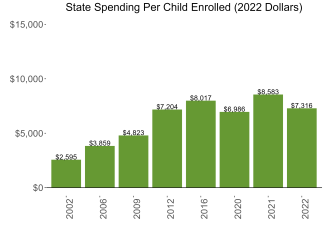
During the 2021-2022 school year, Vermont preschool enrolled 7,541 children, an increase of 947 from the prior year, as the program began to recover from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. State spending totaled $55,171,586 down $1,426,216 (3%), adjusted for inflation since last year. State spending per child equaled $7,316 in 2021-2022, down $1,267 from 2020-2021, adjusted for inflation. Vermont met 7 of 10 quality standards benchmarks.
What's New
In December 2022, Vermont was awarded a federal Preschool Development Grant Birth through Five (PDG B–5) renewal grant for $7,744,080. Funds are planned to be used to support the state’s early childhood system which includes subgrants going to local communities to support mental health care for children and families and support for the early childhood workforce.
There was a mix of in-person and remote instruction during the 2020-2021 school year and Fall 2021. In 2021-2022, pre-K monitoring site visits began using the newly created joint agency pre-K monitoring system.
Background
In 1987, Vermont created the Vermont Early Education Initiative (EEI), an annual competitive grant program to finance early education opportunities for at-risk 3- to 5-year-olds. In 2007, legislation expanded publicly funded prekindergarten education for 4-year-old children in public schools and private programs and provided funding through the state’s Education Fund, similar to K–12, pro-rated based on a model of 10 hours per week.
Starting in 2014, Act 166, required all public school districts to offer Universal Prekindergarten (UPK) for every 3-, 4-, and 5-year-old child not enrolled in kindergarten, for a minimum of 10 hours per week for 35 weeks annually. UPK was fully implemented beginning in the 2016-2017 school year, with pre-K provided through school district operated programs and in contractual partnerships with state-approved public and private programs. Funding for Act 166 is a mix of federal, state, and local dollars.
Act 166 also requires an annual legislative evaluation of the state’s pre-K efforts that includes the number of children and programs participating in UPK, child progress monitoring data, and quality rating and improvement system (QRIS) level information. All Vermont state pre-K programs are required to attain at least four of five stars in Vermont’s QRIS, Step Ahead Recognition Systems (STARS), or hold NAEYC accreditation. STARS requires structured observations of classroom quality using the ECERS or CLASS. Licensed educators with an endorsement in early childhood education and/or early childhood special education are required to be lead teachers in all public school UPK classrooms. For private UPK programs, the licensed educator is required to oversee lead teachers in private UPK classrooms to ensure implementation of UPK education for each child.
The Vermont Agency of Education (AOE) and Agency of Human Services (AHS) completed the process of designing a new joint-agency Pre-K Monitoring System that builds upon existing monitoring systems and procedures to assess the quality of the state’s approved private and public UPK programs.
Vermont Universal Prekindergarten Education (Act 166)
Access
Resources
| Total state pre-K spending | $55,171,586 |
| Local match required? | No |
| State Head Start spending | $0 |
| State spending per child enrolled | $7,316 |
| All reported spending per child enrolled* | $8,468 |
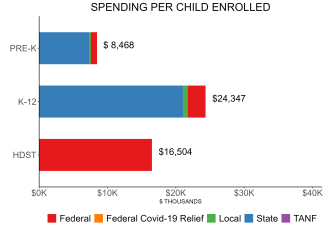
Pre-K programs may receive additional funds from federal or local sources that are not included in this figure. K–12 expenditures include capital spending as well as current operating expenditures. Head Start per-child spending includes funding only for 3- and 4-year-olds.
Vermont Quality Standards Checklist
| Policy | Requirement | Benchmark | Meets Benchmark? |
|---|---|---|---|
For more information about the benchmarks, see the Executive Summary and the Roadmap to State pages. | 7benchmarks met | ||
| Early Learning & Development Standards Benchmark | Comprehensive, aligned, supported, culturally sensitive | Comprehensive, aligned, supported, culturally sensitive | |
| Curriculum Supports Benchmark | Approval process & supports | Approval process & supports | |
| Teacher Degree Benchmark | BA (public); BA for lead teacher, AA for classroom teacher (nonpublic) | BA | |
| Teacher Specialized Training Benchmark | ECE, CD, Elem. Ed. with ECE, ECE SpEd (public); ECE, CD, ECE SpEd (nonpublic) | Specializing in pre-K | |
| Assistant Teacher Degree Benchmark | HSD | CDA or equivalent | |
| Staff Professional Development Benchmark | 6 credit hours/5 years (teachers); 15 hours/year (assistants); PD plans; Coaching (public and some nonpublic) | For teachers & assistants: At least 15 hours/year; individual PD plans; coaching | |
| Maximum Class Size Benchmark | 20 (3- & 4-year-olds) | 20 or lower | |
| Staff to Child Ratio Benchmark | 1:10 (3- & 4-year-olds) | 1:10 or better | |
| Screening & Referral Benchmark | Vision, hearing, health & more | Vision, hearing & health screenings; & referral | |
| Continuous Quality Improvement System Benchmark | Structured classroom observations; Data used for program improvement | Structured classroom observations; data used for program improvement | |

